
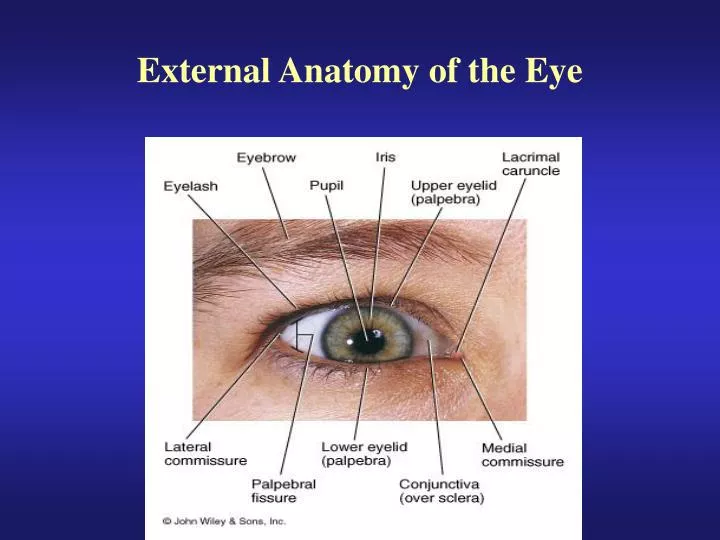
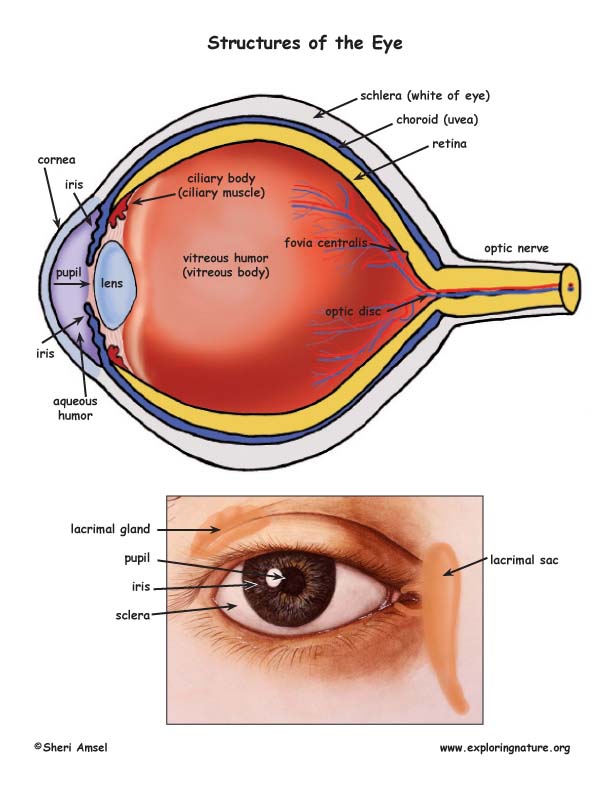
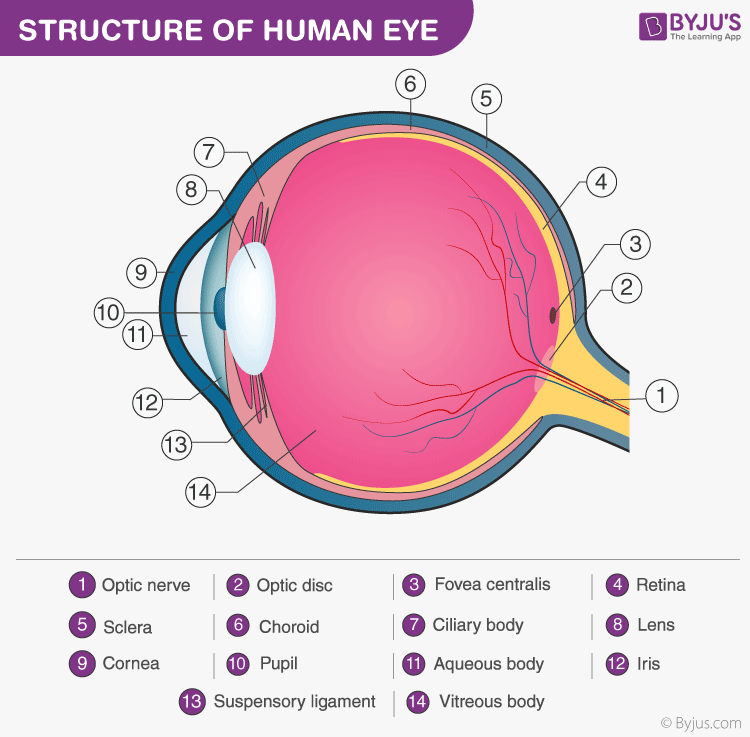
Six of these are responsible for the movement of the eye, with the seventh being responsible for the movement of the superior eyelid. In total, there are seven extraocular muscles. The vitreous body contains vitreous humour.Impaired drainage of aqueous humour can result in glaucoma The anterior and posterior chambers contain aqueous humour, which is constantly produced and drained from the eye.There are three fluid-filled areas within the eye: the anterior chamber, posterior chamber and vitreous body. It supports the neural layer and is continuous throughout the entire eye The pigmented layer lies between the neural layer and the choroid.The area where the optic nerve enters the retina is called the optic disc this area contains no photoreceptors The fovea contains the highest concentration of photoreceptors in the retina and is responsible for high acuity vision. The centre of the posterior aspect of the retina is called the macula, within which lies the fovea. The neural layer is composed of photoreceptors and is deficient in the anterior portion of the eye.The inner layer contains the retina, which is made of neural and pigmented layers. The iris is a structure containing a central aperture (the pupil) which contains smooth muscle that controls its diameter.The choroid is a layer of connective tissue which contains the blood vessels that supply the retina.The ciliary body is attached to the lens via the suspensory ligaments it controls the shape of the lens and forms the aqueous humour.The vascular layer is composed of the ciliary body, choroid and iris. The sclera, which covers the rest of the eye, is white.The cornea is located in the centre of the anterior aspect of the eye and is transparent.The fibrous layer is the outermost layer and consists of the cornea and sclera, which are continuous with one another. The eye can be divided into fibrous, vascular and inner layers. Bones of the orbit Contents of the orbitĪny space within the orbit which is not otherwise occupied is filled with orbital fat. Lateral wall: the anterior section is formed from the zygomatic bone, with the posterior section consisting of the greater wing of the sphenoid boneįigure 1.Floor: the majority is formed by the orbital part of the maxilla, with a minor contribution from the zygomatic and palatine bones.Medial wall: lacrimal, maxilla, ethmoid and sphenoid bones.Roof: the orbital part of the frontal bone, with a small contribution from the sphenoid bone.They form a pyramidal structure with the apex facing posteriorly (Figure 1). The bony orbit is composed of seven bones. You might also be interested in our Anatomy Flashcard Collection which contains over 2000 anatomy flashcards in addition to advanced features such as spaced repetition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
