
Valve is closed unless pressure inside the ventricle pushes it open Both systole and diastole are equally important for moving blood effectively though the heart and through the blood circulation circuits.Ībove: Animated heart pumping with the ventricles shown open.
/human-heart-circulatory-system-598167278-5c48d4d2c9e77c0001a577d4.jpg)
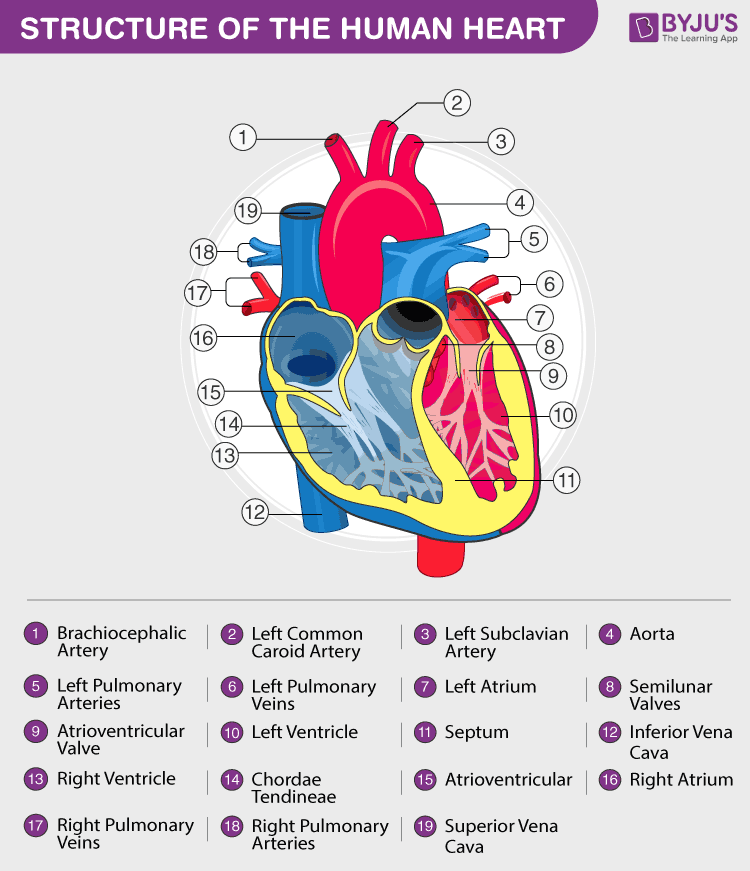
Heart valves are either open or they are closed based on whether the heart muscle of the ventricles is contracting, ventricular systole, or the heart muscle of the ventricles is not contracting, ventricular diastole. The AV valves are also called the tricuspid valve and the bicuspid valve (aka the mitral valve) these names describe the number of cusps that make them up (tri= 3 cusps bi= 2 cusps). The aortic valve and pulmonary valve are sometimes called semilunar valves since they are composed of three crescent-shaped cusps. There are four valves in the heart: two that separate the atria from the ventricles on both the right and left sides ( atrioventricular valves), and two that separate the ventricles from their associated arteries ( aortic valve and pulmonary valve).

Tricuspid valve (aka right atrioventricular valve) drains blood from the right atrium when it is open during ventricular diastoleīlood moves into this chamber through the tricuspid valve (aka right atrioventricular valve) during ventricular diastole blood moves out of this chamber through the pulmonary valve during ventricular systole Mitral valve (aka left atrioventricular valve aka bicuspid valve) drains blood from the left atrium when it is open during ventricular diastoleīlood moves into this chamber through the mitral valve (aka left atrioventricular valve aka bicuspid valve) during ventricular diastole blood moves out of this chamber through the aortic valve during ventricular systoleįrom superior vena cava and inferior vena cava oxygen-poor blood Between the right and left atria is tissue called the interatrial septum and between right and left ventricles is tissue called the interventricular septum. The right and left sides are separated by septa.

The right side of the heart and the left side of the heart are isolated from each other (each belongs to a separate circuit - see the Circulation Through the Heart section below). The atria are the two superior chambers of the heart and the ventricles are the two inferior chambers of the heart. The heart is divided into four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
